Part 2: How to Integrate LangGraph with an MCP RAG Server for Smarter AI Agents?
Integrate a LangGraph AI agent with an MCP-powered RAG server to enable dynamic tool discovery, RAG-first workflows, and scalable education-focused AI assistants.
Introduction
In Part 1, we built a modular MCP RAG Server with Pinecone and OpenAI, exposing it as a self-describing tool with rag_mcp_tools.json.
Purpose
In this part, we'll connect a LangGraph AI agent to that server. The client will:
- Dynamically discover the MCP tools using the validated
rag_mcp_tools.json - Execute a RAG-first workflow to retrieve academic content
- Use retrieved context to generate accurate, grounded answers
Why MCP RAG vs Traditional RAG?
Traditional RAG Limitations
Traditional RAG pipelines are tightly coupled to the client:
- You hardcode the retrieval endpoint and schema
- Changing the vector store or retriever requires code modifications
- Multiple agents need separate integrations for the same RAG service
MCP RAG Server Advantages
- Self-describing tools: Automatically exposes a machine-readable spec (
rag_mcp_tools.json) - Dynamic discovery: Any MCP-compatible agent can consume it without manual wiring
- Loose coupling: Swap vector stores or retrieval logic without breaking clients
- Multi-agent ready: One MCP RAG Server serves multiple AI agents simultaneously
- Schema validation: Ensures consistent input/output contracts for production-grade deployments
How the MCP RAG Server Works?
1. User Query → MCP Client
The LangGraph client sends a query via the MCP protocol.
2. Tool Discovery via rag_mcp_tools.json
The client first discovers the server's tools and validates the schema.
3. Retriever → Pinecone
The server embeds the query, performs a vector similarity search in Pinecone, and fetches the top matching academic content.
4. Return Context via MCP
The server wraps the retrieved documents in the defined DocumentSearchResponse schema and sends it back through MCP.
5. LLM Answer Generation
The LangGraph client feeds the retrieved content into the LLM, ensuring context-grounded responses.
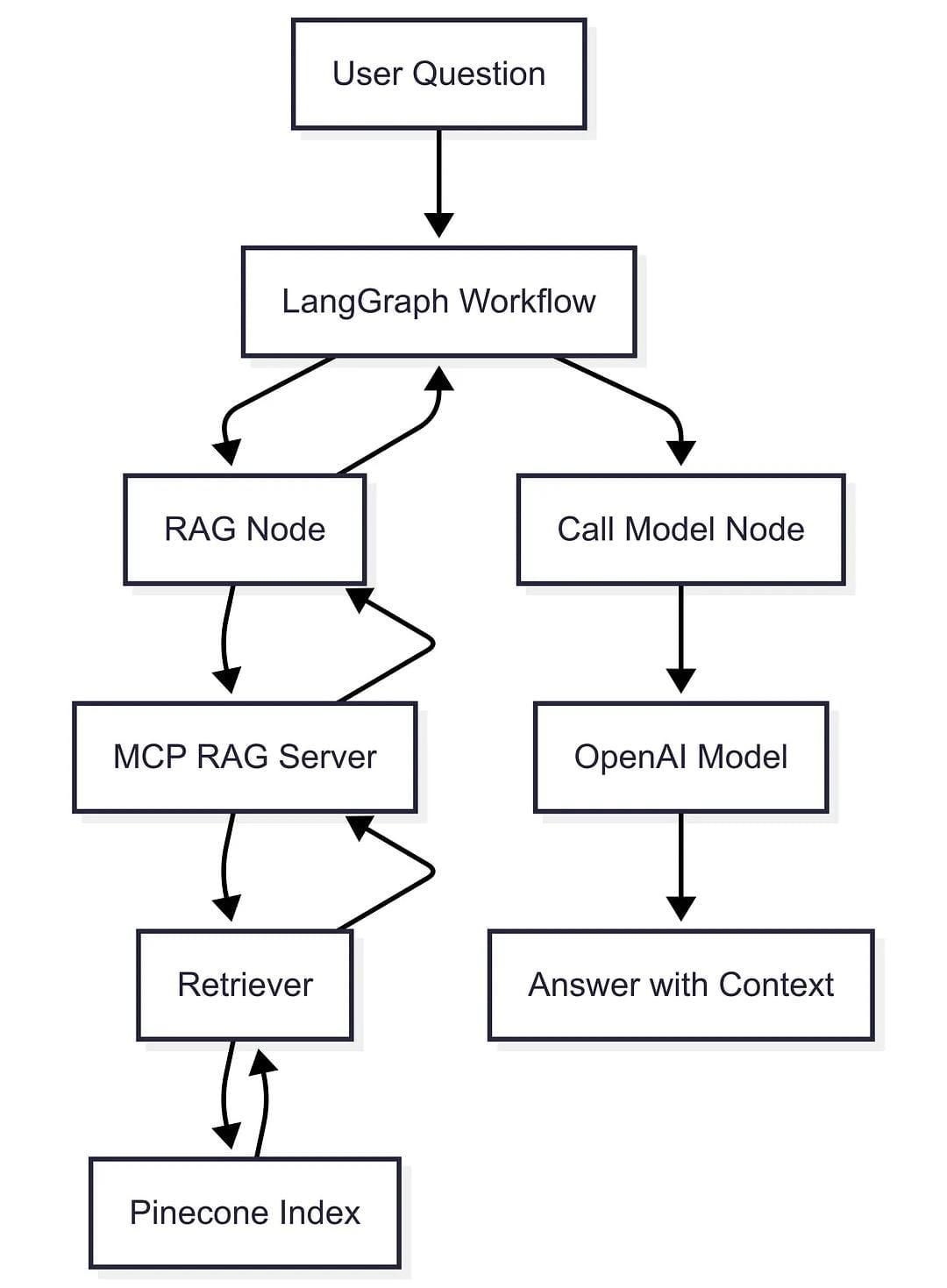
Step 1: Define Graph State (state.py)
Tracks both the conversation and retrieved study materials, ensuring context flows into the AI model for accurate, RAG-powered responses.
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
class GraphState(MessagesState):
retrieved_docs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]]
Step 2: Connect to MCP Tools (nodes.py)
MultiServerMCPClient dynamically loads the MCP RAG tool using rag_mcp_tools.json. This aligns with MCP's plug-and-play architecture, letting your AI agent consume tools without manual wiring.
import os
from .state import GraphState
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage
client = MultiServerMCPClient({
"education_rag": {
"url": os.getenv('RAG_MCP_SERVER_URL', "http://localhost:8001/mcp"),
"transport": "sse",
}
})
class AgentNodes:
def __init__(self):
self.model = init_chat_model("openai:gpt-4o")
self.tools = None
async def call_model(self, state: GraphState):
if self.tools is None:
self.tools = await self.get_tools()
if state.get('retrieved_docs'):
state["messages"].append(
AIMessage(content="Retrieved study materials:\n" + str(state['retrieved_docs']))
)
response = self.model.invoke(state["messages"])
state["messages"].append(response)
return state
async def get_tools(self):
if self.tools is None:
self.tools = await client.get_tools()
return self.tools
Step 3: Build LangGraph Workflow (graph.py)
Enforcing a RAG-first execution ensures every answer is grounded in the academic content retrieved from the MCP RAG Server.
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START
from .state import GraphState
from .nodes import AgentNodes
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
def extract_query(messages):
for m in reversed(messages):
if isinstance(m, HumanMessage):
return m.content
return ""
class WorkflowManager:
def __init__(self):
self.workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
self.nodes = AgentNodes()
async def _setup_workflow_graph(self):
tools = await self.nodes.get_tools()
rag_tool = next(t for t in tools if t.name == "search_relevant_documents")
async def run_rag(state: GraphState):
query = extract_query(state["messages"])
rag_result = await rag_tool.ainvoke({"query": query})
state["retrieved_docs"] = rag_result
return state
self.workflow.add_node("rag", RunnableLambda(run_rag))
self.workflow.add_node("call_model", self.nodes.call_model)
self.workflow.add_edge(START, "rag")
self.workflow.add_edge("rag", "call_model")
Step 4: Run the Client
This step validates the end-to-end LangGraph + MCP RAG pipeline, ensuring your AI agent can use rag_mcp_tools.json for reliable tool discovery and produce context-aware answers.
1. Set the MCP server URL
RAG_MCP_SERVER_URL=http://localhost:8001/mcp
2. Start the client app and send a query
"Explain Newton's laws of motion."
3. Expected flow
- RAG Node calls the MCP RAG Server
- Retrieves study materials
- Model generates grounded response using retrieved context
Conclusion
- Successfully integrated a LangGraph client with the MCP RAG Server
- Implemented a RAG-first AI workflow leveraging validated
rag_mcp_tools.json - Demonstrated dynamic tool discovery and context-grounded answer generation
This client setup shows why MCP RAG outperforms traditional RAG. The use of rag_mcp_tools.json provides a contract-driven integration that guarantees schema validation, multi-agent compatibility, and loose coupling. This is the foundation for scalable, modular AI tutoring and education systems.
Next: If you haven't built the server yet, check out Part 1, where we create the MCP RAG Server and validate it with rag_mcp_tools.json for dynamic tool discovery.
The author is the Founder of Shark AI Solutions which specializes at building production grade value added solutions using AI